Topic outline
-
BAB 1206: BASIC BIOCHEMISTRY

Basic biochemistry module is designed to equip the learner with knowledge, skills and attitude to enable them to develop a good understanding of nutrition, conduct their research project, participate in nutrition and health related studies.
The prerequisite modules include; Human anatomy and physiology, Principles of human nutrition, and physical sciences. The module takes 60 contact hours: 37 hours for theory and 23 hours for practical. Learners undertaking this module will have both theory and practical assessments. Formative assessment will be in the form of continuous assessment tests, assignments, clinical and field assessments and promotional examination whereas summative assessment will be done in form of final qualifying examination.-
Click this link to access your timetable:
-
BASIC BIOCHEMISTRY Quiz
THIS CAT WILL BE DONE ON 11TH DECEMBER 2025 FROM 11-12PM
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS
-
-
 Module Competency
Module CompetencyProvide the learner with basic concept of biochemistry and biochemical metabolism; and to appreciate the role of biochemistry in nutrition; health and disease.
Module DescriptionThis is a first year module design to introduce learners to the course of Basic Biochemistry. It includes: Introduction to Biochemistry: meaning of terms; role of biochemistry in provision of energy and synthesis of various substances; role hormones in regulation of metabolism. Carbohydrates; structure and classification of carbohydrates; properties of carbohydrates; carbohydrate metabolism; glycolysis of carbohydrates; hexose monophosphate pathway; TCA and electron transport; tissue specificity in relation to carbohydrate metabolism and storage; the role of gluconeogenesis; glycogen; glycogenesis and glucogenolysis in organism; regulation of carbohydrate metabolism; metabolic disorders of carbohydrate metabolism; Lipids: meaning of terms; classification of lipids; structure and nomenclature of fats; fatty acids; lipids and acylglycerols; wastes; complex and derivatives; saponification; rancidity; steroids and their functions; cholesterol metabolism; oxidation; ketogenesis and storage; significance of cholesterol in health; metabolism of fat and lipids; functions of lipids; inter-conversion of carbohydrates; fat and protein; disorders of lipid/fat metabolism. Protein: meaning of terms; building block of proteins; amino acids classification; protein structure; protein conformation and denaturation; protein synthesis; properties of proteins; metabolism of proteins; transamination; inter-conversion of amino acids; functions of proteins in the body; disorders of protein metabolism; inter-conversion of carbohydrates and proteins. Enzymes: meaning of term isoenzymes; structures of enzymes; classification of enzymes; occurrence and functions in food systems; factors affecting activity; properties of enzymes; mode of action; enzyme role in biochemical reactions. Nucleic acid; meaning of terms; occurrence of nucleic acids; chromosome; structure and functions of DNA and RNA; nucleotide structure derivatives; differences between nucleosides and nucleotides; protein synthesis. Bioenergetics: meaning of terms; functions of energetics; sources of energy and inter-convertibility; laws of thermodynamics; free energy release from food and energy bonds; oxidation–reduction enzymes and electron transfer; chemical energy formation and transfer. Hormones: meaning of terms; organization of mammalian hormone systems; functions of various hormones; secretion; mode of action and regulation of hormones; role of nucleic adenosine monophosphate on secretion and action of hormones; clinical disorders of hormone deficiencies and excesses. Muscles: types and functions of muscles; structure of muscles; muscle contraction; biochemical and physical changes of muscle. Emerging issues and trends in biochemistry: Identification of trends; challenges and coping mechanisms.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this module, you will have gained sufficient skills to;- Demonstrate understanding of metabolism of major nutrients
- Explain the role of enzymes in nutrient metabolism and in provision of energy
- Explain the mechanism of protein synthesis
- Demonstrate understanding on the role of hormones in nutrient metabolism and regulation
- Explain the disorders of abnormal metabolism and hormones disturbance
The lecturers taking you through this module is Francis Maina and Simon Osonga. Their email addresses are fwaweru@kmtc.ac.ke and sosonga@kmtc.ac.ke respectively. They can also be reached through 0713730995 and 0721700916 respectively. However, if you have a technical problem relating to interacting with the platform, you can write an email to elearning@kmtc.ac.ke. Someone will respond to you as soon as possible
Performance Tasks
Within the various units and topics in the module, there are tasks that you are supposed to attempt and submit for marking. Some of them are not meant for submission. For those that are meant for submission, you are encouraged to be very keen to observe due date because once the date lapses, you will not be able to submit the same. Calling support line will not help you on this. If you are not able to upload an assignment, seek help well in advance before the due date. Otherwise, this will not be used as an acceptable reason for not submitting on time.These tasks are divided into two as follows:(i) Main Tasks that comprise of quizzes and written assignment
(ii) Sub tasks that comprise group discussion and clinical logs.
Learning Requirements
For effective and smooth learning, it is expected of you to be computer proficient. Additionally, to satisfactorily complete this module, it is required of you to;- Submit assignment and required tasks on time
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.
- Sit for CAT’s when scheduled, and
- Sit in Exam at the end of the session.
-
a) Introduction
This unit gives an overview of what biochemistry entails as well as the roles of biochemistry

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, you will have achieved the following objectives;
- Understand what biochemistry entails
- State the roles of biochemistry

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 Quizzes: 2 -
a) Review Questions/Unit Activity
1. Describe the saturated and unsaturated fats in your diet
2. List foods that may contain transfats?
3. List the two families of essential fatty acids and give example of each.
4. Discuss conditions that may lead to ketosis.
5. Explain how lipids are used to supply energy to the body.
6. Explain the β-oxidation pathway and its significance in energy production.
7. Name enzymes responsible for fatty acid catabolism

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
- Describe how biochemistry is interrelated with other disciplines e.g. nutrition
- Why is the knowledge of biochemistry is also important in diagnosing a disease
- State four macromolecules studied in biochemistry
(ii) Sub -Tasks
Discuss the various hormones and the mechanisms through which they regulate carbohydrates metabolism
Assignments: 2 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 -
a) Introduction
This unit gives an overview of carbohydrates in terms of its classification, structures, uses and physico chemical properties
b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to:
- Identify and classify carbohydrates
- Name and draw structures of common monosaccharides and disaccharides
- List the sources and uses of common monosaccharides and disaccharides
- Explain reactions of monosaccharides
- Explain the physical and chemical properties of common polysaccharides

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 Quiz: 1 -
a) Review Questions
Define Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis. What are the inputs and outputs of each of the pathways?
If both pathways were simultaneously active within a cell it would constitute a "futile cycle" that would waste energy. How does the cell prevent this?
Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis.
Explain the role of insulin and glucagon in control of blood glucose
GNG is associated with ketosis. Explain.
Explain the three metabolic fates of pyruvate in living organisms.
Explain the role of Krebs cycle in energy generation?
Define oxidative phosphorylation.
Write an equation summarizing the Krebs cycle
- How many ATP are produced in the formation of acetyl CoA?
 fab fa-twitter-square
fab fa-twitter-square
b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Read and make notes on how glycolysis is regulated
(ii) Sub -Tasks
With a structure, show all the enzymes and transformations that occur in the Embden Meyerhof pathway
Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Definition 1: Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives, and substances related biosynthetically or functionally to these compounds
Definition 2: Lipids are organic compounds that are readily soluble in non-polar solvent (e.g. ether) but not in polar solvent (e.g. water).
Examples of lipids are waxes, oils, sterols, cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides (fats), and phospholipids

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, you will have achieved the following objectives;
- Identify lipid structures
- Describe the functions and uses of lipids
- Explain the reactions of lipids

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 Assignment: 1 -
a) Review Questions
Describe the saturated and unsaturated fats in your diet
List foods that may contain transfats?
List the two families of essential fatty acids and give example of each.
Discuss conditions that may lead to ketosis.
Explain how lipids are used to supply energy to the body.
Explain the β-oxidation pathway and its significance in energy production.
- Name enzymes responsible for fatty acid catabolism

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
- Explain oxidative rancidity of fatty acids and how it can be prevented.
- Explain hydrogenation of fatty acids. Why are vegetable oils hydrogenated?
- Explain the effects of saturated and trans fatty acids to a person’s health.
(ii) Sub -Tasks
Discuss ketoacidosis
Discuss the disorders of lipid/fat metabolism.
Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Proteins are polymers of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. They can be distinguished from fats and carbohydrates by containing nitrogen. Other components include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, Sulphur, and sometimes phosphorus. The type and the sequence of amino acids in a protein are specified by the DNA. The sequence of amino acids is important since it determines the overall structure and function of a protein. Proteins are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's cells, tissues, and organs; and each protein has unique functions

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, you shall be able to;
- Understand the classification of amino acids
- Explain the structures of proteins
- Explain the denaturation of proteins
- Explain the metabolism of proteins
- Explain the classification of proteins and their functions

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 Assignment: 1 -
a) Review Questions
1.Describe the functions of proteins
2. Explain obligatory nitrogen loss from the body and how it relates to amino acid requirement.
3. Discuss protein classification and give examples
4. Draw and explain the formation of a peptide bond.
5. Discuss the methods used to determine protein quality
6. How does the body eliminate excess nitrogen?
7. Define negative nitrogen balance. What factors contribute to it?
8. Explain transamination reactions in protein metabolism.
9. What is the function of urea cycle?
10. Explain factors that increase Blood urea nitrogen.
11. Explain three ways in which amino acid ‘carbon skeletons” are utilized in energy production
12. List two hormones involved in protein metabolism.
13. Explain phenylketonuria (PKU).
14. Explain why the urea cycle enzymes increase during acute starvation

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Name and classify the 20 standard amino acids and give their 3-letter symbols
Analyze your community’s diet and discuss the sources of protein in it.
(ii) Sub -Tasks
1. Identify the main sources of protein in your diet and discuss its quality.
2. Is your diet deficient in protein or does it contain excess protein. Discuss the consequences of each case.

Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Enzymes; - are specialized proteins that are involved in catalysis i.e. they spread up biological reaction. There are 2 types of enzymes depending on where they are produced. They include; intracellular enzymes which are used in the cell where they are produced. Extracellular enzymes are produced by other cells and are secreted to other parts of the body where they are utilized e.g. digestive enzyme.
Zymogen – enzymes which are produced in their inactive forms and they have to be activated before they are able to function e.g.pepsinogen.
Zymase – enzymes produced ready for action-Amylase.
Substrate – substance upon which enzymes acts.
Active site of an enzyme - a small region on the enzyme where a substrate binds for catalysis to take place.

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to;
- Explain the term iso-enzymes
- Describe the structure of enzymes, classification and functions
- Highlight factors affecting enzymatic activities
- State the properties of enzymes and mode of action
- Explain the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 -
a) Review Questions
Describe the characteristics of the active site
What are enzymes? Discuss their nature.
Write note on cofactors and coenzymes.
- Give classification and nomenclature of enzymes

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Describe properties of enzymes
(ii) Sub -Tasks
What are cofactors? Give examples.
Assignments: 2 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Nucleic acids are high molecular weight polymers which occur in every living cell. Their main function is storage and transmission of genetic information.
Two classes of nucleic acid are distinguished according to types of CHO they contain.
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
DNA is a major constituent of chromosome located in the nucleus of the cell but small amount is associated with cell organelle such as chloroplast and mitochondria.
Nucleic acid is polymer of nucleotides and hence they may be called polynucleotide sequence

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, you will have achieved the following objectives
- Define terms used describe the occurrence of nucleic acids
- State the functions of DNA and RNA
- Differentiate between nucleosides and nucleotides
- Explain the sequence of proteins synthesis in the nucleus

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 -
a) Review Questions
What enables cells to have different forms and perform different functions?
What is the primary function of DNA?
What role do proteins have in a cell?
What is the basic unit of DNA and how are these units arranged?
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
What are the four possible nitrogen bases found in DNA and what are their abbreviations?
Which nitrogen bases are purines and which are pyrimidines and what is the difference between them?
Which scientists proposed the Double Helix structure for DNA and when?
- What is the backbone of the DNA structure?

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Differentiate between DNA and RNA
What brings translation to an end
What is anticodon and what is its function(ii) Sub -Tasks
[Discussion forum tool and chat tool below will be used for carrying out group work..]
Assignments: 2 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Bioenergetics is the study of energy transformations in living matter. Matter and energy are distributed about the Universe and the Earth, and in similar fashion throughout you and all your cells. These distributions are dynamic; energy undergoes transfer, so too does matter, from one place to another. The transfer of matter and energy can be spontaneous, or not. Every living cell has the ability, by means of suitable catalysts, to derive energy from its environment, to convert it into a biologically useful form, and to utilize it for driving life processes that require energy. Part of this study will cover thermodynamics as applied to biological systems which are largely non-equilibrium systems with others being near equilibrium systems. This is different from classical thermodynamics which deals mainly with heat energies in equilibrium systems

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to;
- Explain the factors influencing nutrient intake
- Explain factors that influence nutrient availability
- Explain factors influencing nutrient utilization

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 -
a) Review Questions
Define the term bioenergetics?
State four forms of energy transfer will always
Highlight five forms of energy within the body are;
- State five characteristics of 2nd law of bioenergetics reactions

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Describe the process of transduction
Discuss the three Levels of bioenergetics
(ii) Sub -Tasks
[Discussion forum tool and chat tool below will be used for carrying out group work..]
Assignment: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 Forum: 1 -
a) Introduction
Hormones are regulatory substances produced in an organism and transported in tissue fluids such as blood to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action. Is any member of a class of signaling molecules produced by glands in multicellular organisms that are transported by the circulatory system to target distant organs to regulate physiology and behavior

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to;
- State the organization of mammalian hormone system
- Explain the functions of various hormones
- Describe the secretion, mode of action and regulation of hormones
- Explain the role of nucleic adenophosphate on the secretion action
- List the clinical disorders of hormone deficiencies and excesses

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 -
a) Review Questions
- What is the primary function of hormones?
- What are the classifications of hormones?
- What are the three types of interactive effects hormones can have?
- What are the types of responses that a hormone can produce in a target cell?
- Which hormone(s) is(are) produced by this gland?
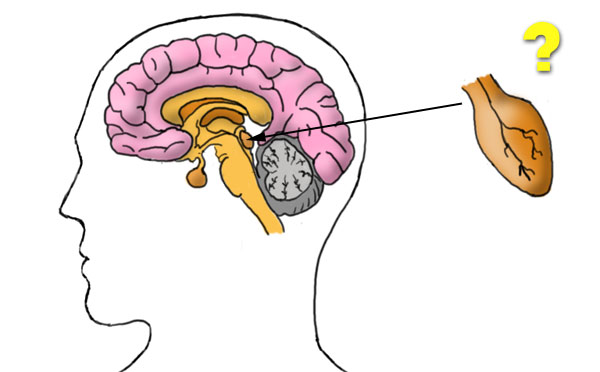

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
What is the primary function of the hypothalamus? What area of the brain does it primarily control?
Which organ system is primarily responsible for regulating metabolism, mood and growth?
Does the endocrine system generate a slow or fast response to maintain homeostasis?(ii) Sub -Tasks
[Discussion forum tool and chat tool below will be used for carrying out group work..]
Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Muscles is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the muscle dermal layer of embrogonic germ cell. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that moves past each other and change the size of the cell

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to;
- List the types and functions and muscles
- Describe the structure of muscles, contraction, biochemical and physical changes

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 Assignment: 1 -
a) Review Questions
What are the mechanical and physiological functions of the skeletal system?
Explain the biochemical reasoning behind muscle fatigue.
Which cell type is specialized for contraction and generation of force?
What are the 3 types of muscles?
- Tendons connect __________ to bone

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
Explain the biochemical reasoning behind muscle fatigue.
What are the differences between an isometric contraction and an isotonic contraction?
(ii) Sub -Tasks
[Discussion forum tool and chat tool below will be used for carrying out group work..]
Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1 -
a) Introduction
Biochemistry has progressed from a purely structural subject to a physical science. Over the last decade the field of biochemistry has made great strides in invention and innovation. this unit aims at understanding emerging issues and trends in biochemistry field

b) Unit Objectives
By the end of this unit, the learner shall be able to;
- Emerging issues and trends,
- Challenges posed by emerging issues and trends,
- Coping mechanisms and strategies

To proficiently complete this unit, you ought to make sure you spend quality time and purpose to;c) Unit Learning Requirements
- Carry out all tasks within the sections and subsections
- Participate in discussion forums as and when they are scheduled.
- Participate in chat sessions as and when they are scheduled.

Lesson: 1 -
a) Review Questions
State the various emerging issues and trends
- State the challenges posed by emerging issues and trends

b) Performance Tasks
(i) Main Tasks
What are the positive and negative consequences of biotechnology and nano technology
(ii) Sub -Tasks
Read on Biotechnology and nanotechnology
Assignment: 1 Forum: 1 Chat: 1 File: 1
